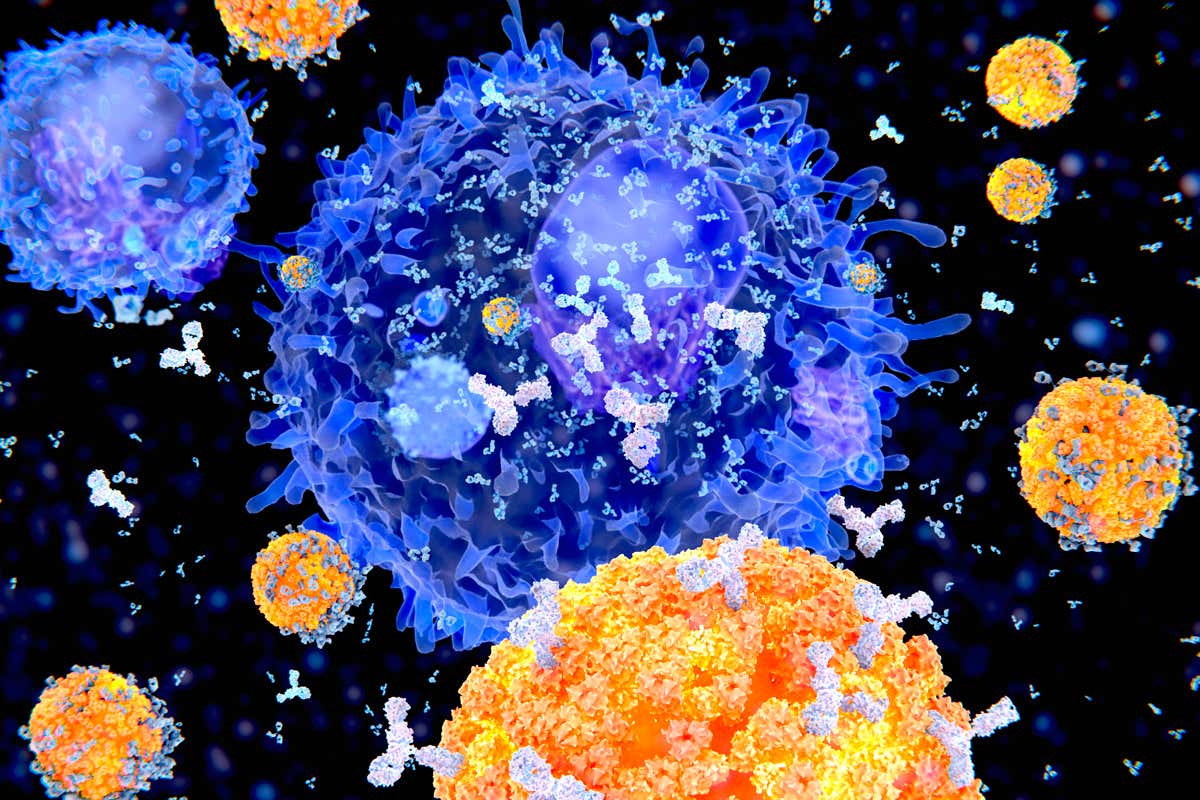
Antibodies have become a buzzword in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. There has been increased interest in antibodies and how you can help deal with the Coronavirus. These immune proteins help fight off viruses and bacteria and protect the body from getting sick in the future. However, there is a lot of information about antibodies you may not know. Here are some essential things you need to know about antibodies.
What are antibodies
These are protective proteins produced by the body’s immune system when it detects harmful substances called antigens. They recognize infectious invaders like bacteria and viruses and help the body eliminate them. An antibody response can take several weeks to function optimally. Despite being slow to develop, antibodies offer long-term protection. There are unique antibodies that defend the body against an antigen. Even those that don’t block infections directly have value.
How do antibodies work?
Image source: https://unsplash.com/photos/rnr8D3FNUNY
Antibodies are y-shaped proteins that develop during an infection or in response to a vaccine. The antibody can recognize and bind to antigens to trigger the body’s immune response and mobilize other cells to fight the invading antigen. Once the immune system has eliminated the antigen, it forms antibody-producing memory cells that remain active after recovery.
However, the challenge of targeting viruses is that they often mutate. The mutations change the shape of viral proteins and limit the antibody’s effectiveness. This is because antibodies require form complementary to function well. When designing neutralizing antibodies, scientists need to know how the virus changes to ensure they target viral proteins or segments of a protein that are less likely to have mutations.
How to engineer antibodies to enhance performance

Image source: https://unsplash.com/photos/wIP4uP_-xQE
Biotech scientists have developed an antibody enhancement toolkit. This happens when molecular engineers apply lessons learned from decades of antibody design and development to engineer an antibody. The antibody attributes will depend on its precise three-dimensional structure, which relies on the sequence of DNA letters in the antibody gene.
During custom antibody production, a scientist can tweak the structure of an antibody by modifying genes to create an antibody that’s easier to manufacture. Other changes can develop antibodies that stay longer in the body and have a high affinity for the target antigens. Custom antibodies can be raised against custom peptides specially selected by Cambridge Research Biochemicals (CRB) or the customer’s protein to generate target-specific antibodies.
Not all antibodies are created equal.

Image source: https://unsplash.com/photos/xX0NVbJy8a8
The effectiveness of antibodies against viruses depends on how strongly it binds. The immune system can create thousands of different antibodies that bind to different proteins on a virus or various parts of the same protein. Some antibiotics may not deter the virus, while others may block critical proteins.
Antibodies in some people with viral infection may rise too late or to fight off the virus. In other cases, the antibodies will bind tightly to a virus but fail to neutralize it. If you experience any of these scenarios, there are different ways you can accelerate the protection provided by antibodies.
Getting a vaccine is one approach you can augment or strengthen your natural antibody response. Vaccines are based on inactivated viruses or viral antigens. They can prompt the immune system to recognize a virus and produce memory B cells against it to guard against future infections. Getting a vaccine offers long-lasting active immunity, but it can take weeks or months for the protection to develop,
The alternative is to manufacture neutralizing antibodies that target the virus and inject them into the body to prevent the disease. These therapeutic antibodies offer rapid protection, though passive immunity can only last a few minutes before the natural process removes the injected antibodies.
How to provide passive immunity
There are different ways of using neutralizing antibodies to treat a viral infection. The simplest way is to collect blood plasma from donors who have recovered from illness and give it to people infected with the same virus. However, sometimes Cornville convalescent plasma varies in its potency and quality. The plasma from one recovered patient can also only treat a few people at most.
It’s possible to manufacture neutralizing antibodies at a large scale using the same techniques used to produce other types of antibody-based therapies. Start by isolating and purifying the target antigens, then injecting this antigen into mice with the humanized immune system. Finish by testing the mice-produced antibodies to find those that bind with high affinity to the target. You can insert the genes that code for the high-affinity antibodies into the cell lines designed to function as antibody factories.
You can use antibody genes from individuals who effectively respond to a virus. Scientists can find genes that produce highly potent neutralizing antibodies by isolating and testing plasma cells or memory B cells from these people.
What is an antibody test?

Image source: https://unsplash.com/photos/CfS6A4U5g8M
This serology test measures the level of antibodies in the blood to highlight past infection and the need for a booster vaccine. The antibody tests are a valuable measure of past illnesses and the impact of a vaccination program. When a healthcare provider tests a blood sample for antibodies, they can get a negative result if the person has no antibodies or the level is too low. However, a negative antibody doesn’t mean you are not protected. Some people take longer to increase the antibody than others until it reaches the level of testing positive.
Bottom line
Antibodies play a crucial role in protecting the body against diseases. They recognize and eliminate foreign invaders like bacteria and viruses. Recently, there have been significant improvements in antibody manufacturing that makes it. These improvements have allowed scientists to redesign biotech manufacturing to make it leaner, more flexible, and more productive.